JAC 12th Physic Importnat Question: Some important questions of class twelfth NCERT Here you can see and read chapter-wise questions. The questions given here are very important for the students and all the students who are looking for important questions of Physics in class 12th and those students who are going to give the Jharkhand Board i.e. JAC Board exam, they are at the right place. Students can get many important questions from here for their board exam. Along with the questions, answers will also be given for the students, which students can read from here.

JAC 12th Physic Importnat Question Pdf Download
MCQs on Class 12 Chapter 1 Electric Charges and Fields
1. If the sizes of charged bodies are very small compared to the distances between them, we treat them as ____________.
- Zero charges
- Point charges
- Single charge
- No charges
Answer: (b) Point charges
Explanation: If the sizes of charged bodies are very small compared to the distances between them, we treat them as point charges.
2. The force per unit charge is known as ____________.
- Electric current
- Electric potential
- Electric field
- Electric space
Answer: (c) Electric field
Explanation: The force per unit charge is known as the electric field.
3. State true or false: The total charge of the isolated system is NOT conserved.
- True (b) False
Answer: (b) False
Explanation: As per the conservation of charges, it is said that the total charge of the isolated system is always conserved.
4. What is the dielectric constant of a metal?
- -1
- 0
- 1
- Infinite
Answer: (d) Infinite
Explanation: The dielectric constant of metals is infinite. The dielectric constant of metal is infinite, as the net electric field inside the metal is zero.
5. If the charge of 1 C is placed at a distance of 1 m from another charge of the same magnitude in a vacuum, it experiences an electrical force repulsion of magnitude ____________

6. The quantisation of charge indicates that
- Charge, which is a fraction of charge on an electron, is not possible
- A charge cannot be destroyed
- Charge exists on particles
- There exists a minimum permissible charge on a particle
Answer: (a) Charge, which is a fraction of charge on an electron, is not possible
Explanation: The quantisation of charge means that when we say something has some charge, we mean by that that how many times the charge of electrons it has. Because the whole charge is associated with an electron.
7. The property which differentiates two kinds of charges is called ____________.
- Equality of charge
- Polarity of charge
- Fraction of charge
- None of the option
Answer: (b) Polarity of charge
Explanation: The property which differentiates two kinds of charges is called polarity of charge.
8. ————— gives the information on field strength, direction, and nature of the charge.
- Electric current
- Electric flux
- Electric field
- Electric potential
Answer: (c) Electric field
Explanation: Electric field gives the information on field strength, direction, and nature of the charge.
9. Choose the correct answer.
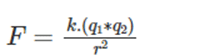
This is given by which law?
- Faraday’s law
- Newton’s law
- Coulomb’s law
- Fleming’s law
Answer: (c) Coulomb’s law
Explanation:
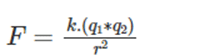
is given by Coulomb’s Law.
10. What happens when a glass rod is rubbed with silk?
- gains protons from silk
- gains electrons from silk
- gives electrons to silk
- gives protons to silk
Answer: (a) gains protons from silk.
Explanation: Excess electrons are transferred from glass to silk when a glass rod is rubbed with silk. Hence, the glass rod becomes positive, and silk becomes negative.
MCQs on Class 12 Chapter 2 Electrostatic Potential and Capacitance
1. The process in which a region is made free from any electric field is known as _____________.
- Electrostatic forcing
- Electrostatic binding
- Electrostatic shielding
- None of the options
Answer: (c) Electrostatic shielding
Explanation: Electrostatic shielding is a phenomenon seen when a Faraday cage is used to block the effects of an electric field.
2. The formula for electrostatic potential is _____________.
- Electrostatic potential = Work done*charge
- Electrostatic potential = Work done/charge
- Electrostatic potential = Work done+charge
- Electrostatic potential = Work done-charge
Answer: (b) Electrostatic potential = Work done/charge
Explanation: The formula for electrostatic potential is Electrostatic potential = Work done/charge.
3. 1 Volt = _____________ style-type: lower-alpha;”>
· 1 Coulomb
· 1 Newton / 1 Coulomb
· 1 Joule / 1 Coulomb
· 1 Newton / 1 meter
Answer: (c) 1 Joule / 1 Coulomb
Explanation: 1 V = 1 Joule / 1 Coulomb
4. The work done in moving a unit positive test charge over a closed path in an electric field is _____________.
- Always 1
- Infinite
- Zero
- Negative
Answer: (c) Zero
Explanation: We say electrostatic forces are conservative in nature since the work done in moving a unit positive test charge over a closed path in an electric field is zero.
5. The electrostatic potential on the perpendicular bisector due to an electric dipole is _____________.
- Zero
- 1
- Infinite
- Negative
Answer: (a) Zero
Explanation: The electrostatic potential on the perpendicular bisector due to an electric dipole is zero.
6. A surface that has the same electrostatic potential at every point on it is known as _____________.
- Equal-potential surface
- Same potential surface
- Equi-magnitude surface
- Equipotential surface
Answer: (d) Equipotential surface
Explanation: Equipotential surface is a surface formed by the locus of all the points which are at the same potential. Equipotential surfaces do not intersect with each other and are closely spaced in the region of strong electric fields and vice-versa.
7. The work done against electrostatic force gets stored in which form of energy?
- Thermal energy
- Kinetic energy
- Potential energy
- Solar energy
Answer: (c) Potential energy
Explanation: The work done against electrostatic force gets stored in the form of potential energy.
8. Dielectrics are _____________
- Conducting substances
- Non-conducting substances
- Semi-conducting substances
- None of the option
Answer: (b) Non-conducting substances
Explanation: Dielectrics are non-conducting substances.
9. The electric potential inside a conducting sphere _____________
- is zero
- increases from centre to the surface
- decreases from centre to the surface
- remains constant from centre to the surface
Answer: (d) remains constant from centre to the surface.
Explanation: The electric potential inside a conducting sphere remains constant from centre to the surface.
10. The capacity of the parallel plate capacitor increases when
- area of the plate is decreased
- area of the plate is increased
- distance between the plates increases
- None of the option
Answer: (b) area of the plate is increased
Explanation: The capacity of the parallel plate capacitor increases when the area of the plate is increased.
MCQs on Class 12 Chapter 3 Current Electricity
1. What is the order of magnitude of the resistance of a dry human body?
- 10 Ω
- 104 Ω
- 10 MΩ
- 10 μΩ
Answer: (b) 104 Ω
Explanation: It is known that the resistance of a dry human body is 10 kΩ = 104 Ω.
2. A silver wire has a resistance of 2.1 Ω at 27.5 °C, and a resistance of 2.7 Ω at 100 °C. What is the temperature coefficient of resistivity of silver?
- 0.0059
- 0.0039
- 0.0129
- 0.0159
Answer: (b) 0.0039
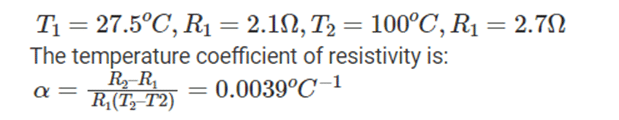
Explanation: Hence, the temperature coefficient of resistivity of silver is 0.0039.
3. The rate of flow of electric charge through any cross-section of a conductor is known as __________.
- Electric flux
- Electric potential
- Electric current
- Electric field
Answer: (c) Electric current
Explanation: The rate of flow of electric charge through any cross-section of a conductor is known as electric current.
4. Mobility is denoted by __________.
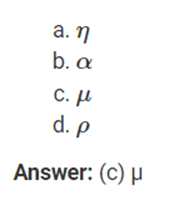
Answer: (c) µ
Explanation: Mobility is denoted by µ.
5. Which of the following is non-ohmic resistance?
- Lamp filament
- Copper wire
- Carbon resistor
- Diode
Answer: (d) Diode is non-ohmic resistance.
Explanation: A non-ohmic resistance is a resistance that does not obey ohm’s law. Among the given options, a diode is a non-ohmic resistance.
6. Unit of conductance is __________.
- Dyne
- Siemen
- Ohm
- Volts
Answer: (b) Siemen
Explanation: Unit of conductance is siemen.
7. Current density is a __________.
- scalar quantity.
- vector quantity.
- dimensionless quantity.
- none of these options
Answer: (b) vector quantity.
Explanation: Current density is a vector quantity.
8. The resistivity of certain metals or alloys drops to zero when they are cooled below a certain temperature, this phenomenon is known as __________.
- Conductivity
- Partial conductivity
- Superconductivity
- Non-conductivity
Answer: (c) Superconductivity
Explanation: The resistivity of certain metals or alloys drops to zero when they are cooled below a certain temperature, this phenomenon is known as superconductivity.
9. State true or false: The total resistance in the series combination is more than the greatest resistance in the circuit.
- True (b) False
Answer: (a) True
Explanation: The total resistance in the series combination is more than the greatest resistance in the circuit.
10. The opposition offered by the electrolyte of the cell to the flow of current through itself is known as __________.
- External resistance
- Internal resistance
- Non-resistance
- None of these options
Answer: (b) Internal resistance
Explanation: The opposition offered by the electrolyte of the cell to the flow of current through itself is known as internal resistance.
MCQs on Class 12 Chapter 4 Moving Charges and Magnetism
1. The magnetic moment of a current I carrying a circular coil of radius r and number of turns N varies as

3. SI unit of the magnetic field is _________.
- Dyne
- Ohm
- Tesla
- Volt
Answer: (c) Tesla
Explanation: The SI unit of the magnetic field is Tesla.
4. When the charged particles move in a combined magnetic and electric field, then the force acting is known as _________.
- Centripetal force
- Centrifugal force
- Lorentz force
- Orbital force
Answer: (c) Lorentz force
Explanation: When the charged particles move in a combined magnetic and electric field, then the force acting is known as Lorentz force.
5. Magnetic field at any point inside the straight solenoid is given as———-
- B = μ0+nI
- B = μ0+n+I
- B = μ0/nI
- B = μ0nI
Answer: (d) B = μ0nI
Explanation: Magnetic field at any point inside the straight solenoid is given as B = μ0nI.
6. Cyclotron is a device used to _________.
- Slow down charged particles
- Accelerate the positively charged particles
- Stop the charged particles
- None of the options
Answer: (b) Accelerate the positively charged particles
Explanation: A cyclotron is a device used to accelerate positively charged particles.
7. 1 Gauss =
- 104 Tesla
- 10-4 Tesla
- 102 Tesla
- 10-2 Tesla
Answer: (b) 10-4 Tesla
Explanation: 1 Gauss = 10-4 Tesla.
8. State true or false: A cyclotron is a device used to accelerate uncharged particles like neutrons.
- True
- (b) False
Answer: (b) False
Explanation: A cyclotron is a device used to accelerate positively charged particles.
9. Lorentz force is given by the formula
- F= q(v + B + E)
- F= q(v – B – E)
- F= q(v * B * E)
- F= q(v * B + E)
Answer: (d) F= q(v * B + E)
Explanation: Lorentz force is given by the formula F= q(v * B + E)
10. The concept of displacement current was introduced by _________.
- Newton
- Ampere
- Maxwell
- Fleming
Answer: (c) Maxwell
Explanation: The concept of displacement current was introduced by Maxwell.
MCQs on Class 12 Chapter 5 Magnetism and Matter
1. A horse-shoe magnet is an example of ________.
- Natural magnet
- Artificial magnet
- Neither natural nor artificial
- None of these options
Answer: (b) Artificial magnet
Explanation: Artificial magnets are man-made magnets. Magnets that are made from iron in different components shapes and sizes for different uses are called artificial magnets.
2. A freely suspended magnet aligns in which direction?
- South-west
- East-west
- North-south
- North-west
Answer: (c) North-south
Explanation: A freely suspended magnet aligns in north-south direction.
3. Which among the following materials display higher magnetic susceptibility?
- Ferromagnetic material
- Paramagnetic material
- Diamagnetic material
- None of these options
Answer: (a) Ferromagnetic material
Explanation: Ferromagnetic materials display higher magnetic susceptibility.
4. A permanent magnet has the capacity to attract
- All substances
- Some substances
- Only ferromagnetic substances
- None of these options
Answer: (c) Only ferromagnetic substances
Explanation: A permanent magnet has the capacity to attract only ferromagnetic substances
5. The SI unit of magnetic flux is
- Dyne
- Tesla
- Weber
- Ohm
Answer: (c) Weber
Explanation: The SI unit of magnetic flux is Weber.
6. Susceptibility is positive for
- Ferromagnetic material
- Paramagnetic material
- Diamagnetic material
- Option (a) and (b)
Answer: (d) Option (a) and (b)
Explanation: Susceptibility is positive for ferromagnetic as well as paramagnetic materials.
7. The magnetic dipole moment of a magnetic dipole is given by the formula ________.
- M = m × 2I
- M = m + 2I
- M = m – 2I
- M = m / 2I
Answer: (a) M = m × 2I
Explanation: The magnetic dipole moment of a magnetic dipole is given by the formula M = m × 2I. Where: m is pole strength and 2I is dipole length directed from S to N.
8. What is the formula to find the work done in rotating the dipole in a uniform magnetic field from θ1 to θ2?
- W = MB (cos θ1/cos θ2)
- W = MB (cos θ1 + cos θ2)
- W = MB (cos θ1 – cos θ2)
- W = M+B (cos θ1 – cos θ2)
Answer: (c) W = MB (cos θ1 – cos θ2)
Explanation: The formula to find the work done in rotating the dipole in a uniform magnetic field from θ1 to θ2 is W = MB (cos θ1 – cos θ2).
9. What does a superconductor exhibit?
- Ferromagnetism
- Paramagnetism
- Diamagnetism
- None of these options
Answer: (c) Diamagnetism
Explanation: A superconductor exhibits diamagnetism.
10. State true or false: Magnetic field lines do not form loops.
- True (b) False
Answer: (b) False
Explanation: Magnetic field lines form continuous closed loops
Ch-6 Class 12 Electromagnetic Induction MCQs
1. Which of the following factors is the induced charge in an electromagnetic induction independent of?
- Time
- Resistance of the coil
- Change of flux
- None of the above
Answer: (a) Time
Explanation: The induced charge in an electromagnetic induction is independent of time.
2. Which of the following states that an emf is induced whenever there is a change in the magnetic field linked with electric circuits?
- Lenz’s Law
- Ohm’s Law
- Faraday’s Law of Electromagnetic Induction
- None of the above
Answer: (c) Faraday’s Law of Electromagnetic Induction
Explanation: Faraday’s Law of Electromagnetic Induction states that an emf is induced whenever there is a change in the magnetic field linked with the electric circuits changes.
3. Which of the following gives the polarity of the induced emf?
- Biot-Savart Law
- Lenz’s Law
- Ampere’s circuital Law
- Fleming’s right-hand Rule
Answer: (b) Lenz’s Law
Explanation: Lenz’s Law gives the polarity of the induced emf.
4. Electrical Inertia is the measure of
- Self Inductance
- Mutual Inductance
- Impedance
- None of the above
Answer: (a) Self Inductance
Explanation: Electrical Inertia is the measure of self inductance.
5.Which of the following laws is the consequence of the Law of conservation of energy?
- Lenz’s Law
- Ohm’s Law
- Archimedes Law
- All of the above
Answer: (a) Lenz’s Law
Explanation: Lenz’s Law is the consequence of the Law of conservation of energy.
6. Which of the following apparatus construction uses electromagnetic induction?
- Voltmeter
- Galvanometer
- Generator
- Electric Motor
Answer: (c) Generator
Explanation: The construction of the generator uses the principle of electromagnetic induction.
7. Which of the following factors is the self inductance associated with a coil is independent of?
- induced voltage
- current
- time
- coil resistance
Answer: (d) coil resistance
Explanation: The self inductance associated with a coil is independent of coil resistance.
8. Which of the following rules is used to identify the direction of the current induced in a wire moving in a magnetic field?
- Ampere’s Rule
- Fleming’s Left-Hand Rule
- Fleming’s Right-Hand Rule
- None of the above
Answer: (b) Fleming’s Left-Hand Rule
Explanation: Fleming’s Left Hand Rule is used in identifying the direction of the current induced in a wire moving in a magnetic field.
9. Which of the following statements is true?
- A metal plate can be heated by passing either a direct current or an alternating current through the plate.
- A metal plate can be heated by placing it in a time-invariant magnetic field.
- A metal plate can be heated by placing it in a time-variant magnetic field
- Both (a) and (c)
Answer: (d) Both (a) and (c)
Explanation: A metal plate can be heated by passing either a direct current or an alternating current through the plate or placing it in a time-variant magnetic field.
10. The induced emf is equal to the coefficient of self-inductance is equal to unity, when the rate of change of current is unity.
- True
- False
Answer: (a) True
Explanation: The induced emf is equal to the coefficient of self-inductance is equal to unity, when the rate of change of current is unity.
Ch-7 Class 12 Alternating Current MCQs
1. What is the frequency of the AC Mains in India?
- 60 Hz
- 50 Hz
- 40 Hz
- 30 Hz
Answer: (b)50 Hz
Explanation: The frequency of the AC Mains in India is 50 Hz.
2. An alternating current can be produced by
- Choke Coil
- Dynamo
- Electric Motor
- Transformer
Answer: (b) Dynamo
Explanation: An alternating current can be produced by a dynamo.
3. Which of the following can measure an alternating current?
- Voltmeter
- Ammeter
- Suspended coil galvanometer
- Moving coil galvanometer
Answer: (b) Ammeter
Explanation: Ammeter can measure an alternating current.
4. Which of the following circuits exhibits maximum power dissipation?
- Pure Inductive Circuit
- Pure Capacitive Circuit
- Pure Resistive Circuit
- None of the above
Answer: (c) Pure Resistive Circuit
Explanation: A pure resistive circuit exhibits maximum power dissipation.
5. What happens to the inductive reactance when the frequency of the AC supply is increased?
- Increases
- Decreases
- Remains the same
- Decreases inversely
Answer: (a) increases
Explanation: The inductive reactance of the AC supply increases with the frequency of the AC supply.
6. What happens to the quality factor of an LCR circuit if the resistance is increased?
- Increases
- Decreases
- Remains the same
- None of the above
Answer: (b) Decreases
Explanation: The quality factor of an LCR circuit decreases if the resistance of the circuit is increased.
7. Which of the following statements is true about the LCR circuit connected to an AC source at resonance?
- Voltage across R equals the applied voltage.
- Voltage across R is zero.
- Voltage across C is zero.
- Voltage across L equals the applied voltage.
Answer: (a) R equals the applied voltage.
Explanation: At resonance, R equals the applied voltage.
8.The impedance in the series LCR circuit is minimum at the resonance frequency.
- True
- False
Answer: (a) True
Explanation: The impedance in the series LCR circuit is minimum at the resonance frequency.
9. When is the current in a circuit wattless?
- When the inductance of the circuit is zero.
- When the resistance of the circuit is zero.
- When the current is alternating.
- When both resistance and inductance are zero.
Answer: (b) When the resistance of the circuit is zero.
Explanation: The current in a circuit is wattless when the resistance of the circuit is zero.
10. The power factor is one for which of the following?
- Pure capacitor
- Pure inductor
- Pure resistor
- All of the above
Answer: (c) Pure resistor
Explanation: The power factor is unity for the pure resistor.
Ch-8 Class 12 Electromagnetic Waves MCQs
1. What is the phase difference between electric and magnetic fields in an electromagnetic wave?
- (a) 0
- (b) π
- (c) π/2
- (d) π/4
Answer: (b) π
Explanation: The phase difference between electric and magnetic fields in an electromagnetic wave is π.
2. Which of the following waves have a maximum frequency?
- infrared waves
- gamma rays
- microwaves
- radio waves
Answer: (b) gamma rays
Explanation: Gamma rays have a maximum frequency.
3. According to Maxwell’s Hypothesis, a changing electric field gives rise to?
- Induced EMF
- Electric Field
- Magnetic Field
- Magnetic Dipole
Answer: (c) Magnetic Field
Explanation: A changing electric field gives rise to a magnetic field.
4. Which of the following proves that electromagnetic waves are transverse?
- Reflection
- Diffraction
- Interference
- Polarisation
Answer: (d) Polarisation
Explanation: Only transverse waves can be polarised.
5. Which of the following is used to investigate the structure of solids?
- Gamma Rays
- Infrared Rays
- X-Rays
- Cosmic Rays
Answer: (c) X-Rays
Explanation: X-Rays are used to investigate the structure of solids.
6. Which of the following radiations are used to treat muscle ache?
- Microwaves
- Infrared Rays
- Ultraviolet Rays
- X-Rays
Answer: (b) Infrared Rays
Explanation: Infrared rays are used to treat muscle aches.
7. When is the conduction current the same as the displacement current?
- When the source is ac
- When the source is dc
- When the source is either an ac or a dc
- When the source is neither dc nor ac
Answer: (a) When the source is ac
Explanation: The conduction current is the same as the displacement current when the source is ac.
8. An electromagnetic wave can be produced when the charge is
- moving in a circular orbit
- moving with a constant velocity
- falling in an electric field
- Both (a) and (c)
Answer: (d) Both (a) and (c)
Explanation: An accelerated charge is the source of electromagnetic waves (EMWs). When the charge is in a circular motion, the direction of its velocity continuously changes and thus it is in accelerated motion and produces EMWs. A charge falling in an electric field is accelerated by the electric force and thus produces EMWs.
9. Which waves are used by artificial satellites for communication?
- Infrared rays
- Microwaves
- Radiowaves
- X-Rays
Answer: (b) Microwaves
Explanation: Microwaves are used by artificial satellites for communication.
10. The ratio of contributions made by the magnetic field and electric field components to the intensity of an EM wave is
- 1:1
- c:1
- c2:1
- √c:1
Answer: (a) 1:1
Explanation: The ratio of contributions made by the magnetic field and electric field components to the intensity of an EM wave is 1:1.
Ch-9 Class 12 Ray Optics and Optical Instruments MCQs
1. Which of the following lights deviates the most when it passes through a prism?
- Red Light
- Violet Light
- Neither (a) nor (b)
- Both (a) and (b)
Answer: (b) Violet Light
Explanation: Violet Light deviates the most when it passes through a prism.
2. Which of the following phenomena of light results in a mirage?
- Refraction of light
- Reflection of light
- Total internal reflection
- Diffraction of light
Answer: (c) Total internal reflection
Explanation: Total Internal Reflection results in a mirage.
3. For which of the following is the field of view maximum?
- Concave mirror
- Convex mirror
- Plane mirror
- Cylindrical mirror
Answer: (b) Convex Mirror
Explanation: For convex mirrors, the field of view is maximum.
4. What happens when the light is refracted into a medium?
- Both frequency and wavelength of the light increase
- The wavelength increases but the frequency remains unchanged
- Both wavelength and frequency decrease
- The wavelength decreases but the frequency remains constant
Answer: (b) The wavelength increases but the frequency remains unchanged
Explanation: When the light is refracted into a medium its wavelength increases but the frequency remains unchanged.
5. If a glass prism is dipped in water, what happens to its dispersive power?
- Increases
- Decreases
- Does not change
- No effect
Answer: (b) Decreases
Explanation: If a glass prism is dipped in water, its dispersive power decreases.
6. What should be increased to increase the angular magnification of a simple microscope?
- The power of the lens
- The focal length of the lens
- Lens Aperture
- Object Size
Answer: (a) The power of the lens
Explanation: The power of the lens should be increased to increase the angular magnification of a simple microscope.
7. Which of the following phenomenon is used in optical fibre?
- Refraction
- Diffraction
- Scattering
- Total Internal Reflection
Answer: (d) Total Internal Reflection
Explanation: Total Internal Reflection is used in optical fibre.
8. Which of the following statements is true for total internal reflection?
- Light travels from rarer medium to denser medium
- Light travels from denser medium to rarer medium
- Light travels in water only
- Light travels in the air only
Answer: (b) Light travels from denser medium to rarer medium
Explanation: For total internal reflection, the light must travel from a denser medium to a rarer medium.
9. A convex lens is dipped in a liquid whose refractive index is equal to the refractive index of the lens. Then what is its focal length?
- Focal Length will become zero
- Focal Length will become infinite
- Focal length will reduce, but not become zero
- Remains unchanged
Answer: (b) Focal Length will become infinite
Explanation: The focal length of the lens becomes infinite.
10. For a telescope, the larger the diameter of the objective lens
- Greater the resolving power
- Greater the magnifying power
- Smaller the resolving power
- Smaller the magnifying power
Answer: (a) Greater the resolving power
Explanation: For a telescope, the larger the diameter of the objective lens, the greater the resolving power.
Ch-10 Class 12 Wave Optics MCQs
1. What is the geometric shape of the wavefront that originates when a plane wave passes through a convex lens?
- Converging spherical
- Diverging spherical
- Plane
- None of the above
Answer: (a) Converging Spherical
Explanation: A converging spherical wavefront originates when a plane wave passes through a convex lens.
2. How can the fringe width increase in Young’s double-slit experiment?
- By decreasing the width of the slit
- By reducing the separation of slits
- By reducing the wavelength of the slits
- By decreasing the distance between slits and the screen
Answer: (b) By decreasing the separation of slits
Explanation: The fringe width can be increased in Young’s double-slit experiment by decreasing the separation of slits.
3. What is the locus of all particles in a medium vibrating in the same phase called?
- Fringe
- Wavelet
- Wavefront
- None of the above
Answer: (c) Wavefront
Explanation: The locus of all particles in a medium vibrating in the same phase is called a wavefront.
4. Which of the following factors does the intensity of light depend on?
- Frequency
- Wavelength
- Amplitude
- Velocity
Answer: (c) Amplitude
Explanation: The intensity of light depends on amplitude.
5. Which of the following light phenomena confirms the transverse nature of light?
- Refraction of light
- Diffraction of light
- Dispersion of light
- Polarization of light
Answer: (d) Polarization of light
Explanation: Polarization of light confirms the transverse nature of light.
6. Polaroid glasses are used in sunglasses because
- They are cheaper
- They have a good colour
- They look fashionable
- They reduce the light intensity to half on account of polarization
Answer: (d) They reduce the light intensity to half on account of polarization
Explanation: Polaroid glasses are used in sunglasses because they reduce the light intensity to half on polarization.
7. Two light sources are said to be coherent when both the sources of light emit light of
- The same amplitude and phase
- The same intensity and wavelength
- The same speed
- The same wavelength and constant phase difference
Answer: (d) the same wavelength and constant phase difference
Explanation: Two light sources are said to be coherent when both light sources emit light of the same wavelength and constant phase difference.
8. Which of the following is an application of the Doppler Effect?
- Doppler Radius
- Doppler Spectrometer
- Doppler Velocimeter
- All of the above
Answer: (d) All of the above
Explanation: Doppler Radius, Doppler Spectrometer and Doppler Velocimeter are applications of the Doppler Effect.
9. Who discovered Poisson’s bright spot?
- Fresnel
- Rayleigh
- Fraunhofer
- Poisson
Answer: (d) Poisson
Explanation: Poisson discovered Poisson’s bright spot.
10. Which of the following is conserved when light waves interfere?
- Intensity
- Amplitude
- Phase
- None of the above
Answer: (d) None of the above
Explanation: Intensity, amplitude, and phase are not conserved when light waves interfere.
Class 11 Dual Nature of Radiation and Matter MCQs
1. The emission of electrons does not occur in which of the following?
- Photoelectric Emission
- Thermionic Emission
- Secondary Emission
- X-Ray Emission
Answer: (d) X-Ray Emission
Explanation: The emission of electrons does not take place in X-Ray Emission.
2. What happens to the kinetic energy of the emitted electrons when the light is incident on a metal surface?
- It varies with the frequency of light
- It varies with the light intensity
- It varies with the speed of light
- It varies irregularly
Answer: (a) It varies with the frequency of light.
Explanation: The kinetic energy of the emitted electrons varies with the frequency of light.
3. A photoelectric cell is a device which
- Converts light energy into electricity
- Converts electricity into light energy
- Stores Light energy
- Stores Electricity
Answer: (a) Converts light energy into electricity.
Explanation: A photoelectric cell is a device that converts light energy into electricity.
4. What does a cathode ray consist of?
- Electrons
- Protons
- Photons
- Alpha particles
Answer: (a) Electrons
Explanation: A cathode ray consists of electrons.
5. Who gave the theory of quantization of electric charge?
- J.J Thomason
- William Crookes
- R.A Millikan
- Wilhelm Hallwachs
Answer: (c) R.A Millikan
Explanation: R.A Millikan gave the theory of quantization of electric charge.
6. Which of the following metals is not sensitive to visible light?
- Rubidium
- Sodium
- Caesium
- Cadmium
Answer: (d) Cadmium
Explanation: Cadmium is not sensitive to visible light.
7. Which of the following does the wave theory of light not explain?
- Diffraction
- Photocurrent
- Polarization
- Interference
Answer: (b) Photocurrent
Explanation: Wave theory can explain diffraction, polarization and interference but could not explain the photoelectric effect. The photoelectric effect is explained by a quantum theory which treats light as a particle.
8. Photons are deflected by
- Magnetic field only
- Electric field only
- Electromagnetic field
- None of the above
Answer: (d) None of the above
Explanation: None of the given options deflect photons.
9. The photoelectric effect is based on the law of conservation of
- Energy
- Momentum
- Mass
- Angular momentum
Answer: (a) Energy
Explanation: The photoelectric effect is based on the law of conservation of energy.
10. Photon does not possess
- Energy
- Momentum
- Rest Mass
- Frequency
Answer: (c) Rest Mass
Explanation: Photon do not possess rest mass.
Ch-12 Class 12 Atoms MCQs
1. What did Rutherford’s alpha particle experiment prove?
- Electrons
- Protons
- Neutrons
- Nucleus
Answer: (d) Nucleus
Explanation: Rutherford’s alpha particle experiment proved the existence of the nucleus.
2. Why was Rutherford’s atomic model unstable?
- Electrons do not remain in orbit.
- Nuclei will break down.
- The nucleus repels electrons.
- Orbiting electrons radiate energy.
Answer: (a) Electrons do not remain in orbit.
Explanation: Rutherford’s atomic model was unstable because electrons do not remain in orbit.
3. Balmer series lies in which spectrum?
- Ultraviolet
- Visible
- Infrared
- Partially Visible
Answer: (b) Visible
Explanation: Balmer series lies in the visible spectrum.
4. According to the classical theory, the circular path of the electrons is
- Circular
- Parabolic
- Spiral
- Straight line
Answer: (c) Spiral
Explanation: According to classical theory, the circular path of the electrons is spiral.
5. Electrons in the atom are held to the nucleus by
- Nuclear Force
- Coulomb’s Force
- Gravitational Force
- Van Der Waal’s Force
Answer: (b) Columb’s Force
Explanation: Electrons in the atom are held to the nucleus by Coulomb’s Force.
6. The electrons of Rutherford’s model would be expected to lose energy because
- They jump on the nucleus
- They move randomly
- Radiate electromagnetic waves
- Escape from the atom
Answer: (c) Radiate electromagnetic waves.
Explanation: The electrons of Rutherford’s model would be expected to lose energy because they radiate electromagnetic waves.
7. Who discovered the first spectral series?
- Lyman
- Balmer
- Paschen
- Pfund
Answer: (b) Balmer
Explanation: Balmer discovered the first spectral series.
8. Which of the following did Bohr use to explain his theory?
- Quantization of angular momentum
- Conservation of Quantum frequency
- Conservation of Mass
- Conservation of Linear Momentum
Answer: (a) Quantization of angular momentum
Explanation: Bohr used the quantization of angular momentum to explain his theory.
9. The significant result deduced from Rutherford’s scattering experiment is that
- the whole of the positive charge is concentrated at the centre of an atom
- there are neutrons inside the nucleus
- α-particles are hydrogen nuclei
- electrons are embedded in the atom
Answer: (a) the whole of the positive charge is concentrated at the centre of an atom.
Explanation: The significant result deduced from Rutherford’s scattering is that whole of the positive charge is concentrated at the centre of the atom i.e. nucleus.
10. The first model of the atom was proposed by
- Neils Bohr
- Albert Einstein
- J.J Thompson
- Ernest Rutherford
Answer: (c) J.J Thompson
Explanation: J. J Thompson proposed the first model of the atom.
Ch-13 Class 12 Nuclei MCQs
1. Which of the following quantities is not conserved in a nuclear reaction?
- Mass
- Charge
- Momentum
- None of the above
Answer: (a) Mass
Explanation: Mass is not conserved in a nuclear reaction.
2. A radioactive nucleus emits a beta particle, then the parent and daughter nuclei are
- Isotones
- Isotopes
- Isomers
- Isobars
Answer: (d) Isobars
Explanation: The parent and daughter nuclei are isobars.
3. An electron emitted in beta radiation originates from
- free electrons existing in the nuclei
- inner orbits of an atom
- photon escaping from the nucleus
- decay of a neutron in a nuclei
Answer: (c)photon escaping from the nucleus
Explanation: An electron emitted in beta radiation originates from photons escaping from the nucleus.
4. The light energy emitted by a star is due to
- Joining of nuclei
- Burning of nuclei
- Breaking of nuclei
- Reflection of solar light
Answer: (a) Joining of nuclei
Explanation: The light energy emitted by a star is due to the joining of nuclei.
5. In nuclear reactions, there is a conservation of
- Energy only
- Mass only
- Mass, energy and momentum
- Momentum only
Answer: (d) Momentum only
Explanation: In nuclear reactions, there is a conservation of momentum only.
6. Which of the following are not emitted by radioactive substances?
- Protons
- Electrons
- Gamma Rays
- Helium Nuclei
Answer: (a) Protons
Explanation: Protons are not emitted by radioactive substances.
7. From where are the gamma rays originated?
- The innermost shell of the nucleus
- The outermost shell of the nucleus
- Nucleus
- The outermost shell of the atom
Answer: (c) Nucleus
Explanation: Gamma rays are originated from the nucleus.
8. Sun’s radiant energy is due to
- Nuclear Fusion
- Nuclear Fission
- Photoelectric Effect
- Radioactive Decay
Answer: (a) Nuclear Fusion
Explanation: Sun’s radiant energy is due to Nuclear Fusion.
9. A nucleus undergoes gamma decay due to
- Excess of neutrons
- Excess of protons
- Its excited state
- Large mass
Answer: (d) Its excited state
Explanation: A nucleus undergoes gamma decay due to its excited state.
10. Isotones have the same number of
- Protons
- Electrons
- Neutrons
- All of the above
Answer: (c) Neutrons
Explanation: Isotones have the same number of neutrons.
CH-14 Class 12 Semiconductor Materials MCQs
1. What bonds are present in a semiconductor?
- Monovalent
- Bivalent
- Trivalent
- Covalent
Answer: (d) Covalent
Explanation: Covalent bonds are present in a semiconductor.
2. The number of electrons in the valence shell of a semiconductor is
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
Answer: (d) 4
Explanation: The number of electrons in the valence shell of a semiconductor is 4.
3. What happens to the forbidden energy gap of a semiconductor with the fall of temperature?
- Decreases
- Increases
- Unchanged
- Sometimes decreases and sometimes increases
Answer: (b) Increases
Explanation: The forbidden energy gap of a semiconductor increases with the fall of temperature.
4. In a p-type semiconductor, the current conduction is due to
- Holes
- Atoms
- Electrons
- Protons
Answer: (a) Holes
Explanation: In a p-type semiconductor, the current conduction is due to holes.
5. What is the main function of a transistor?
- Simplify
- Amplify
- Rectify
- All of the above
Answer: (b) Amplify
Explanation: The main function of a transistor is to amplify.
6. In a semiconductor, what is responsible for conduction?
- Electrons only
- Holes only
- Both electrons and holes
- Neither electrons nor holes
Answer: (c) Both electrons and holes
Explanation: Both electrons and holes are responsible for conduction in a semiconductor.
7. What happens to the resistance of semiconductors on heating?
- Increases
- Decreases
- Remains the same
- First increases later decrease
Answer: (b) decreases
Explanation: The resistance of semiconductors decreases on heating.
8. In intrinsic semiconductors at room temperature, the number of electrons and holes are
- Unequal
- Equal
- Infinite
- Zero
Answer: (b) Equal
Explanation: In intrinsic semiconductors, the number of electrons and holes are equal.
9. Which of the following is not a universal gate?
- NOT
- AND
- OR
- NAND
Answer: (d) NAND
Explanation: NAND is not a universal gate.
10. A p-type semiconductor is
- Positively charged
- Negatively charged
- Uncharged
- None of the above
Answer: (c) Uncharged
Explanation: A p-type semiconductor is electrically neutral that is uncharged.
Ch-14 Class 12 Communication System MCQs
1. What purpose does the transducer serve?
- It converts sound signal to electrical signal
- It converts the electrical signal to a sound signal
- It converts electrical signals to magnetic form
- It converts sound signal to magnetic signal
Answer: (b) It converts an electrical signal to a sound signal.
Explanation: A transducer converts an electrical signal to a sound signal.
2. Which of the following is a drawback of the amplitude modulation?
- Noise Reception
- Low Efficiency
- Low Operating range
- All of the above
Answer: (d) All of the above
Explanation: Noise Reception, low efficiency and low operating range are the drawbacks of amplitude modulation.
3. Why audio signals cannot be transmitted?
- Because it has more noise
- The length of the transmitting antenna is very small
- The length of the transmitting antenna is very large
- The signal cannot be amplified for distance communication
Answer: (c) The length of the transmitting antenna is very large
Explanation: Audio signals cannot be transmitted because the length of the transmitting antenna is very large.
4. What happens to the satellite speed when the height of the satellite orbit gets lower?
- Increases
- Decreases
- Remains same
- Both (a) and (b)
Answer: (a) Increases
Explanation: The satellite speed increases as the height of the satellite orbit gets lower.
5. What happens when the frequency deviation is doubled in FM?
- Modulation is doubled
- Modulation is halved
- Carrer swing is halved
- The modulation index is decreased
Answer: (a) Modulation is doubled
Explanation: When the frequency deviation is doubled, the modulation doubles.
6. What happens if the transmission path in PCM is very long?
- Pulse amplitude is increased
- Pulse spacing is reduced
- Pulse width is increased
- Repeater stations are used
Answer: (d) Repeater stations are used
Explanation: Repeater stations are used if the transmission path in PCM is very long.
7. Television signals are
- Amplitude modulated
- Frequency modulated
- Phase modulated
- Both frequency and amplitude modulated
Answer: (d) Both frequency and amplitude modulated
Explanation: Television signals are both frequency and amplitude modulated.
8. What happens when the radio wave reaches the ionizing medium?
- Will bend towards normal
- Will bend away from the normal
- Will follow a straight path
- None of these
Answer: (a) Will bend away from the normal
Explanation: The radio waves reaching the ionizing medium will bend away from the normal.
9. The summation of three sinusoidal waves is equal to
- AM Waves
- FM Waves
- Both (a) and (b)
- Neither of these
Answer: (a) AM Waves
Explanation: The summation of three sinusoidal waves is equal to AM Waves.
10. The space waves that are seriously affected by the atmospheric conditions are known as:
- VHF
- HUF
- MF
- UHF
Answer: (d) UHF
Explanation: The space waves that are seriously affected by atmospheric conditions are known as UHF.

Pdf kaha se download kare?